Blog
NAD⁺ Therapy and Cancer Risk: Separating Theory from Evidence
NAD⁺ therapy has gained attention for its role in cellular energy, DNA repair, and healthy ageing.
Alongside grow...
Five Essential Things I Wish Patients Knew Before Starting Tirzepatide (Mounjaro)
Why “Optimum” Is Not the Same as “Normal” When Measuring Iron Levels in Women
Iron is a critical mineral for overall health, particularly for women who experience menstruation, pregnancy, or other factors that can d...
The Benefits of Curcumin Supplementation
The Complete Guide To IV Therapy
Boost Your Immune System This Season with an IV Immunity Drip from Effect Doctors
How Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Enhances the Benefits of IV Infusions
Dr Will Buxton discusses how combining hyperbaric oxygen therapy alongside an IV drip infusion enhances the impact of both.
...Why My Clients Keep Coming Back for Glutathione, Curcumin & Vitamin C IV Therapy
Senior Nurse Abi talks about the three ingredients that her clients keep coming back for.
...What to Eat While Taking Mounjaro
Starting Mounjaro is a powerful step in your weight loss journey. What you eat alongside it makes all the difference. Dr Will Turner shar...
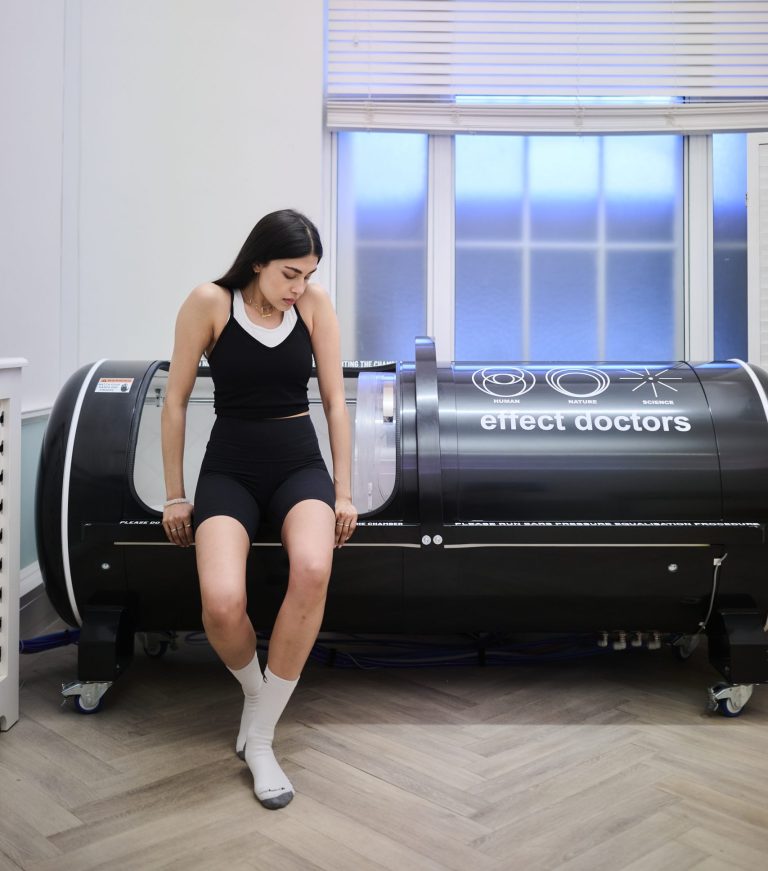
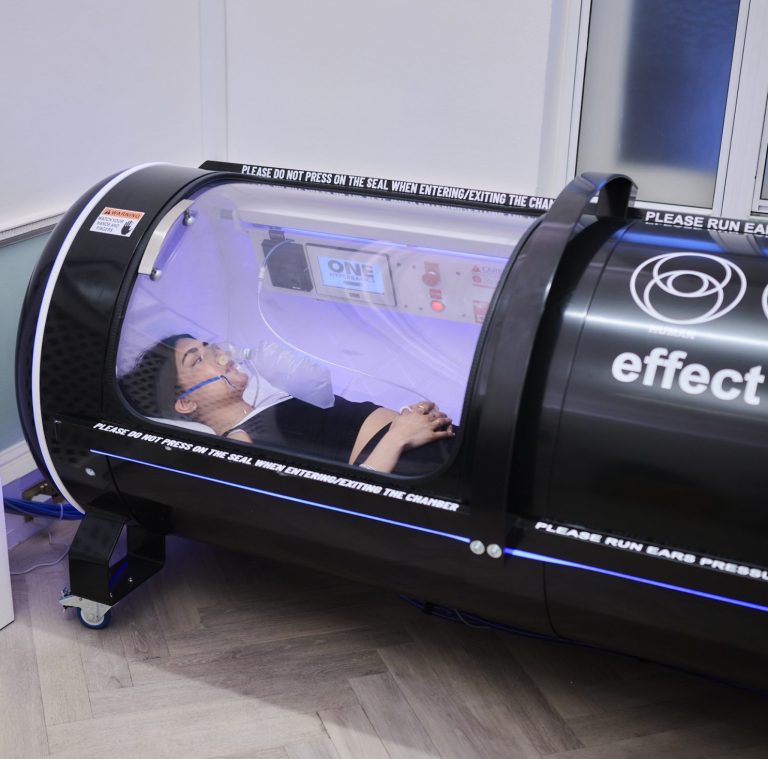
The Science-Backed Power of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
The science is there: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is backed by decades of clinical use and scientific study showing significa...
Hangovers 101: What Causes Them & How to Speed Up Recovery
Most of us have experienced the uncomfortable symptoms of a hangover, but understanding why these symptoms occur can be the difference be...
Iron Deficiency and ADHD: What’s the Connection?
Emerging research suggests a link between iron deficiency and symptoms commonly associated with ADHD, such as brain fog, poor concentrati...
Seven Myths about Weight Loss Drugs Mounjaro and Wegovy.
Mounjaro and Wegovy have transformed the way we approach weight loss—but these medications work best with the right support. In this ar...
Understanding Which Blood Test is Right for You
Blood tests offer a powerful window into your internal health—helping you detect issues early, understand your body better, and make in...
The Silent Fire: How Chronic Inflammation is Damaging Your Health
Maintaining muscle mass while taking Mounjaro
Dr Will Turner talks about how to maintain muscle mass while losing weight using the weight loss drug Mounjaro.
...ALA (Alpha Lipoic Acid) What Is It?
The Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Unlocking the Benefits of NAD+ IV Infusions: A Game-Changer for Cellular Health
How To Keep Your Skin Healthy And Glowing In Winter
Unveiling the Benefits of CoQ10 for Enhanced Health and Vitality
Curcumin IV Supplementation: Elevating Health Naturally
Vitamin C Supplementation: Oral and IV Methods Explored
Our 5 Benefits of having NAD+ Therapy
NAD+ (the oxidised form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is one of the main puzzle pieces in the majority of our biological processe...